Products / Carbon Sequestration
Carbon sequestration refers to capturing and storing atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) to reduce the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere and mitigate the impacts of climate change. The datasets monitor carbon sequestration i.e., the carbon dioxide (CO2) that trees absorb from the atmosphere as they grow, and store this carbon in their wood, leaves, and roots.
Carbon sequestration is important because it helps to reduce the amount of atmospheric CO2, which is a major contributor to climate change. When CO2 is released into the atmosphere through the burning of fossil fuels, it traps heat, leading to an increase in global temperatures. This can have a range of negative impacts, including more frequent heatwaves and droughts, sea level rise, and changes in weather patterns.
Parameters
Above Ground Biomass
All living vegetation above the soil, including stems, stumps, branches, bark, seeds, and foliage.
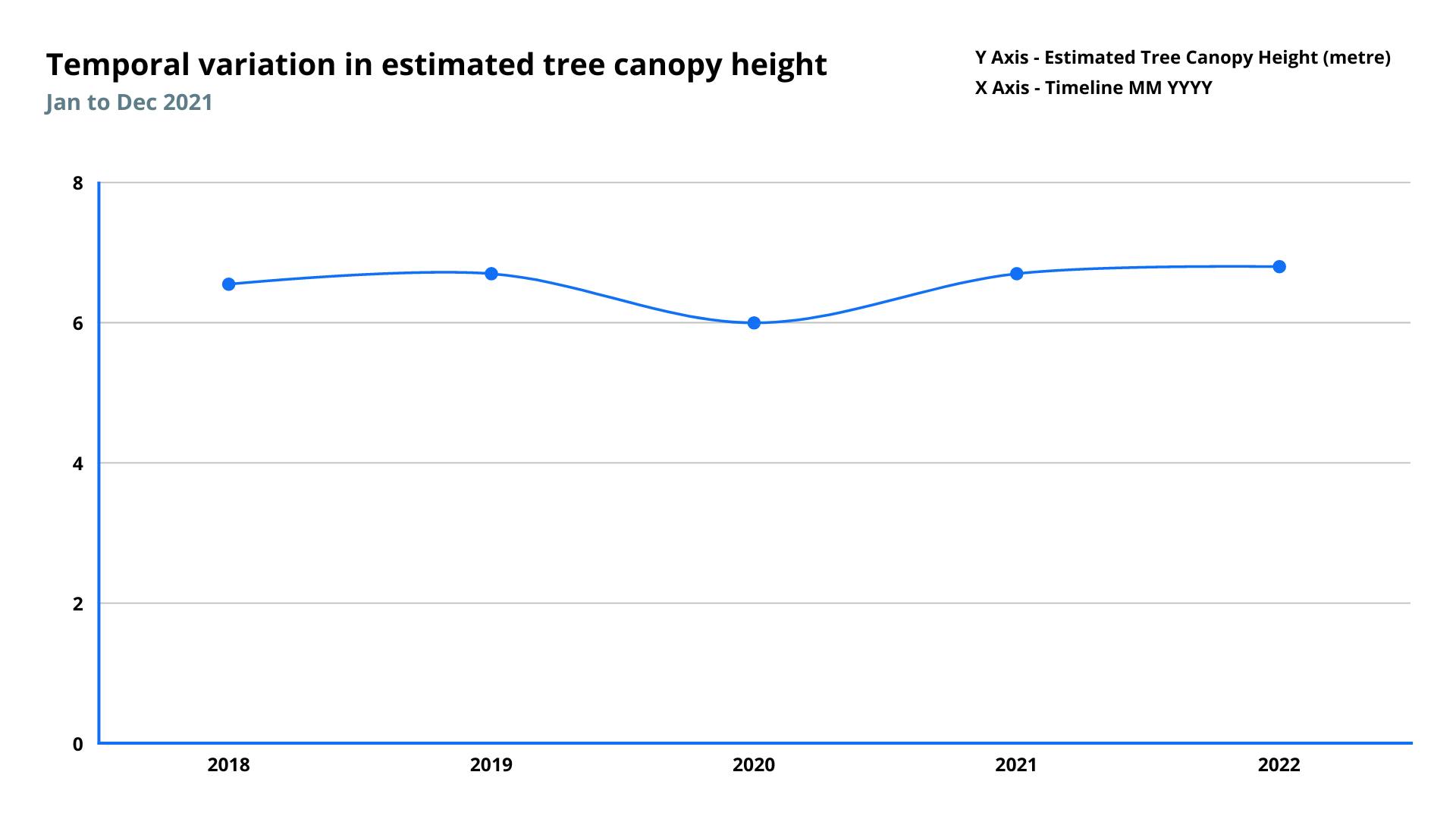
Canopy Height Estimation
Canopy Heights indicate the relative height of canopy surface areas (vertical vegetation profiles).
Carbon Stock
Carbon stock is the amount of carbon stored in a given ecosystem or area. This includes carbon stored in living biomass (such as trees), dead organic matter (such as leaves and wood), and soil.
Green Cover Area
It provides the estimated area covered by green vegetation in square kilometers.
Tree Count
It provides the estimated number of trees at the given location.
Features
Methodology
Satellite data is used to estimate the amount of carbon stored in forests by considering factors such as the type of trees, their size, and other forest characteristics, such as canopy height, the density of vegetation, and the species of trees.
Frequency
Monthly
Spatial resolution
30 meter
Coverage
Global
Data type
Raster
Availability